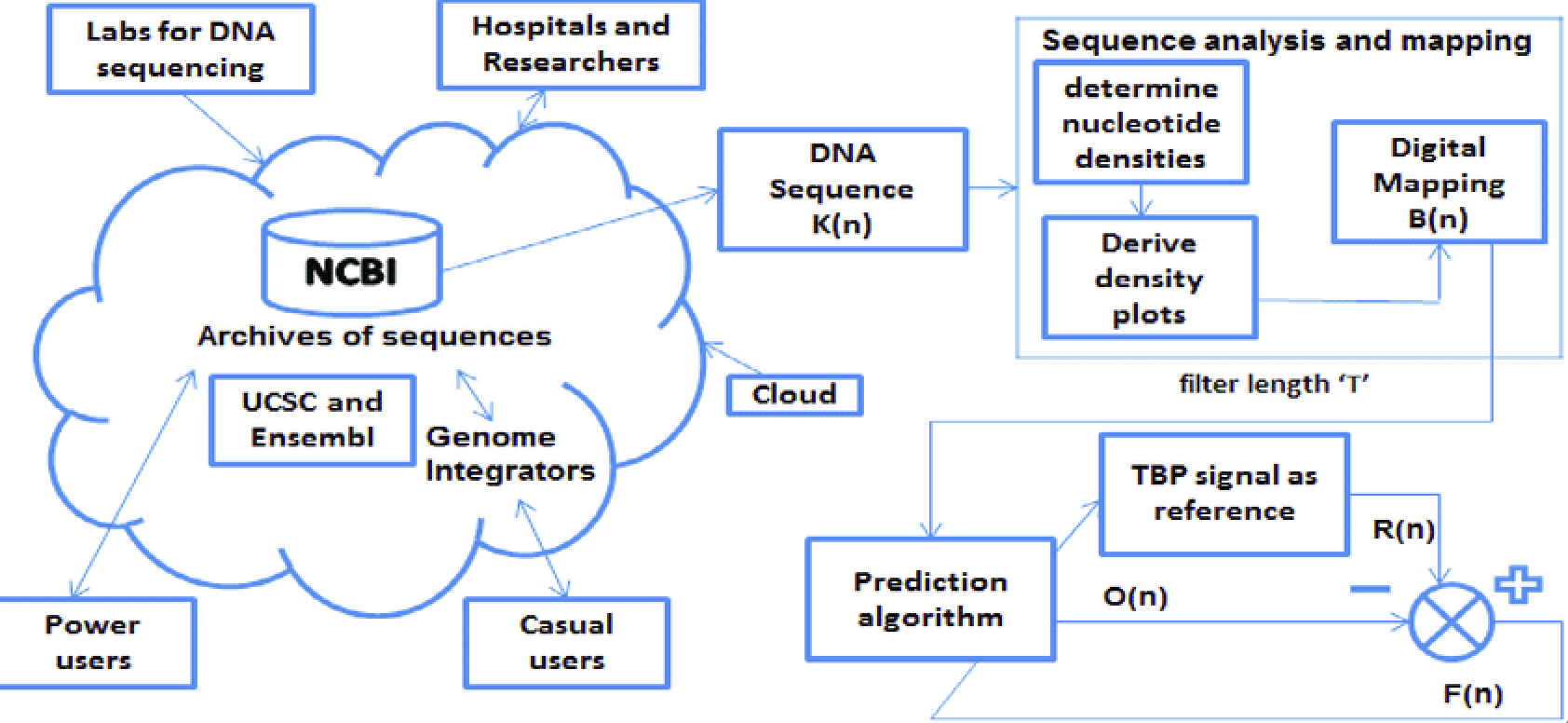
As biology enters the digital age, the frontier of preservation is expanding beyond cryogenic freezers. Traditional biobanks focus on storing physical specimens—cells, tissues, and genetic material—but a new paradigm is emerging: digital biobanking. By archiving entire genomes, transcriptomes, and epigenetic profiles, scientists can preserve the biological essence of an organism as data—ready for analysis, sharing, or even reconstruction.
At Skytyx Biobank, we are building a hybrid infrastructure that merges physical and digital storage. This approach allows us to safeguard not only biological material, but also the informational code that defines life itself.
What Is a Digital Biobank?
A digital biobank is a repository of fully sequenced and annotated biological data. This includes:
- Whole genome and transcriptome sequences
- Epigenetic markers and gene expression profiles
- Linked metadata: species, origin, phenotype, health status, and ecological context
Digital biobanks provide a scalable, durable, and globally accessible format for preserving genetic diversity. While physical samples may degrade or be lost over time, genetic data can be securely stored, duplicated, and analyzed indefinitely.
Why Digital Preservation Matters
Long-Term Stability
DNA and tissue degrade—even under ideal storage conditions. By sequencing and digitizing genetic material, researchers create a permanent record that can be recovered and reanalyzed at any time.
Global Collaboration
Digital data can be shared instantly across institutions and borders, accelerating international research, conservation efforts, and pandemic responses.
Synthetic Reconstruction
Advances in DNA synthesis now allow entire genomes to be reassembled from digital blueprints. Organisms can be recreated or engineered based on stored data alone.
AI-Driven Insights
Large digital biobanks enable the use of artificial intelligence for genome mining, predictive modeling, and discovery of genes linked to disease resistance, adaptation, or productivity.
Approach to Digital Biobanking
Digital biobanking is integrated into every stage of our physical sample workflow. To provide:
- High-throughput genomic and transcriptomic sequencing of preserved samples
- Standardized metadata capture and classification for each specimen
- Secure cloud infrastructure with encrypted backups and blockchain-based access control
- Cross-referenced indexing with physical cryostorage for dual-access capability
This dual system increases resilience, ensures sample traceability, and enables a full-spectrum approach to biotechnology, conservation, and synthetic biology.
Applications of Digital Biobanks
Genomic Libraries for Synthetic Biology
Digitally archived microbial and plant genomes are used to design new drugs, enzymes, or metabolic pathways. Rare genes can be printed and inserted into production strains, bypassing the need for physical access to endangered organisms.
Conservation and De-Extinction
Species under threat can be digitally preserved even from minimal samples. In the future, these genomes may be reconstructed and used to restore lost biodiversity through cloning or gene editing.
Agricultural Innovation
Digital records of landraces and wild crop relatives provide breeders with access to valuable traits—such as drought resistance, pest tolerance, and improved nutritional content—without needing the original seeds or tissues.
Public Health and Biodefense
Pathogen genomes archived during past outbreaks help researchers predict mutation trends, develop diagnostics, and prepare targeted vaccines for future pandemics.
